This article provides users with a systematic understanding of the selection logic for seamless steel pipes, and allows them to further explore specific sub-sectors through anchor points, ultimately achieving a closed loop from knowledge acquisition to product decision-making.
Overview
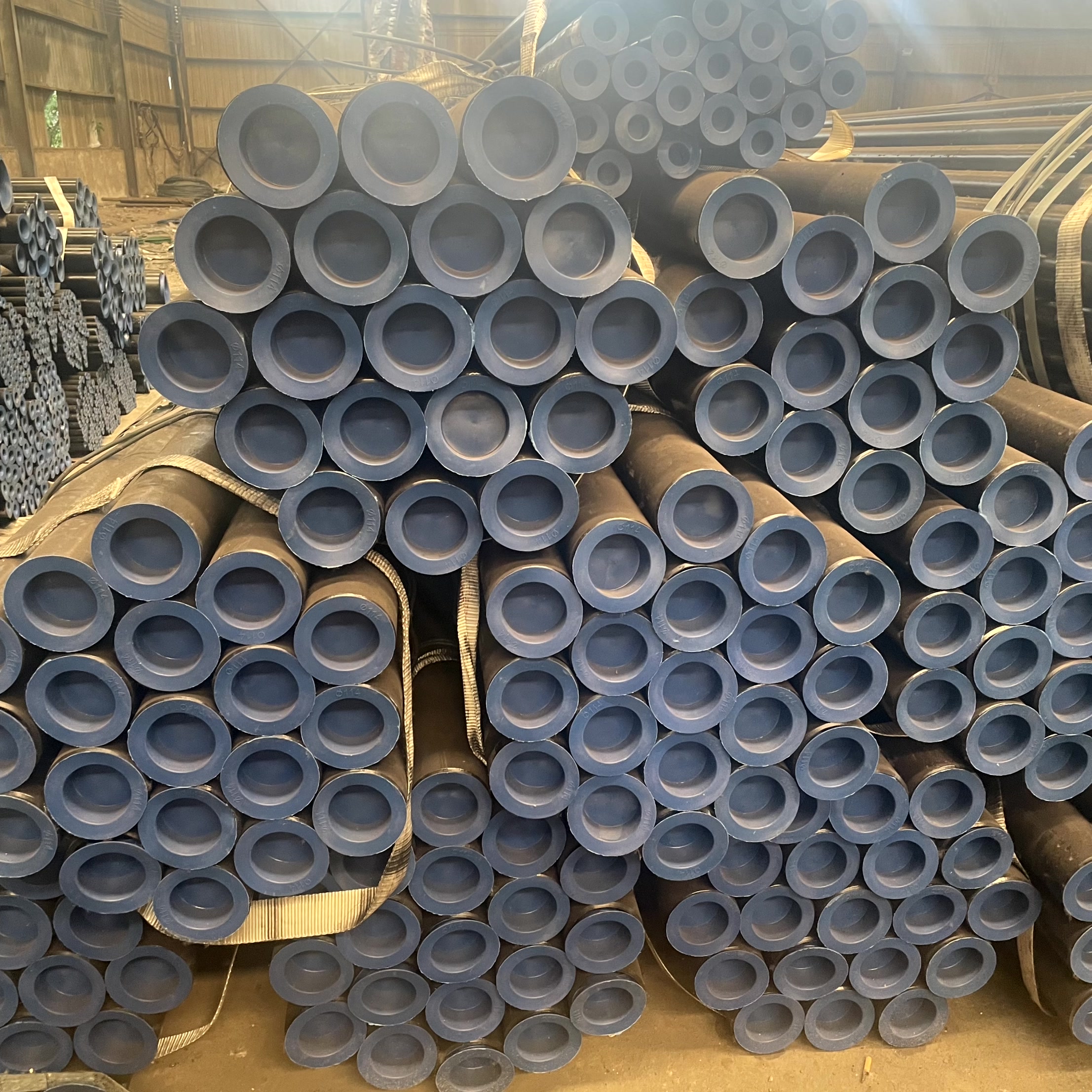
Seamless steel pipes are hollow cross-section tubes manufactured through hot rolling or cold drawing processes. Due to their weld-free structure, they possess the following core advantages:
High strength and pressure resistance: Uniform material distribution allows them to withstand high-pressure environments, reducing the risk of leakage; High dimensional accuracy: Suitable for precision machinery and demanding engineering projects; Wide adaptability: Different materials (carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel) can be customized to meet specific needs.
| Types | Characteristics | Typical Application Scenarios |
| Seamless carbon steel pipe | Low cost, high strength, but generally poor corrosion resistance. | Applications include oil transportation and structural supports. |
| Seamless alloy steel pipe | High temperature resistance, creep resistance, suitable for extreme working conditions | Power plant boilers, chemical reactors |
| Seamless stainless steel pipe | Resistant to acid and alkali corrosion, long service life | Applications: Food processing, marine engineering |
Application scenarios
Applicable high-pressure scenarios include: The oil and gas industry, which involves high-pressure fluid transportation, requires pipelines to meet API standards and withstand high-pressure transport; Chemical systems, which transport corrosive media over long periods, require stainless steel or alloy steel pipes to resist chemical corrosion; Boiler systems, operating in high-temperature steam environments, rely on alloy steel or carbon steel (such as P235GH).
In the fields of structural engineering and mechanical manufacturing: Building supports can be economically solved using seamless carbon steel tubes (such as GB/T 8163 20#); Mechanical shaft components can be made with cold-drawn seamless tubes to ensure precision and wear resistance.
Manufacturing processes and standards
Comparison of manufacturing process and standard process: Hot-rolled tubes are suitable for large-diameter, thick-walled tubes and have high production efficiency; Cold-drawn tubes have higher precision and better surface finish, making them suitable for precision instruments.
International Standards System
GB/T 8163: Chinese standard, specifying that 20# steel is used for general fluid transportation;
EN 10216-1: European pressure piping standard, P235GH steel must pass impact toughness test;
ASTM A106: American carbon steel pipe standard, suitable for high-temperature service.
Selection Guide
Material Selection:(1)P235GH: Preferred for European pressure vessels, suitable for temperatures ≤350℃, such as steam pipelines;
(2)20# steel: Preferred for low-pressure applications at normal temperatures, cost-optimized;
(3)Stainless steel (e.g., 316L): Essential for highly corrosive environments.
Key performance evaluation points:(1)Pressure resistance: Calculate wall thickness according to ASME B31.1;
(2)Temperature resistance: Creep strength of the material needs to be considered in high-temperature scenarios;
(3)Corrosion resistance: Stainless steel + lining process is recommended for acidic media.
Industry Trends
Demand in the new energy sector: Hydrogen transportation requires higher-strength seamless pipes, and geothermal development relies on high-temperature resistant materials;
Intelligent manufacturing: Automated non-destructive testing technology improves quality control efficiency;
Environmental compliance: Pressure equipment must comply with the PED directive to reduce environmental risks.