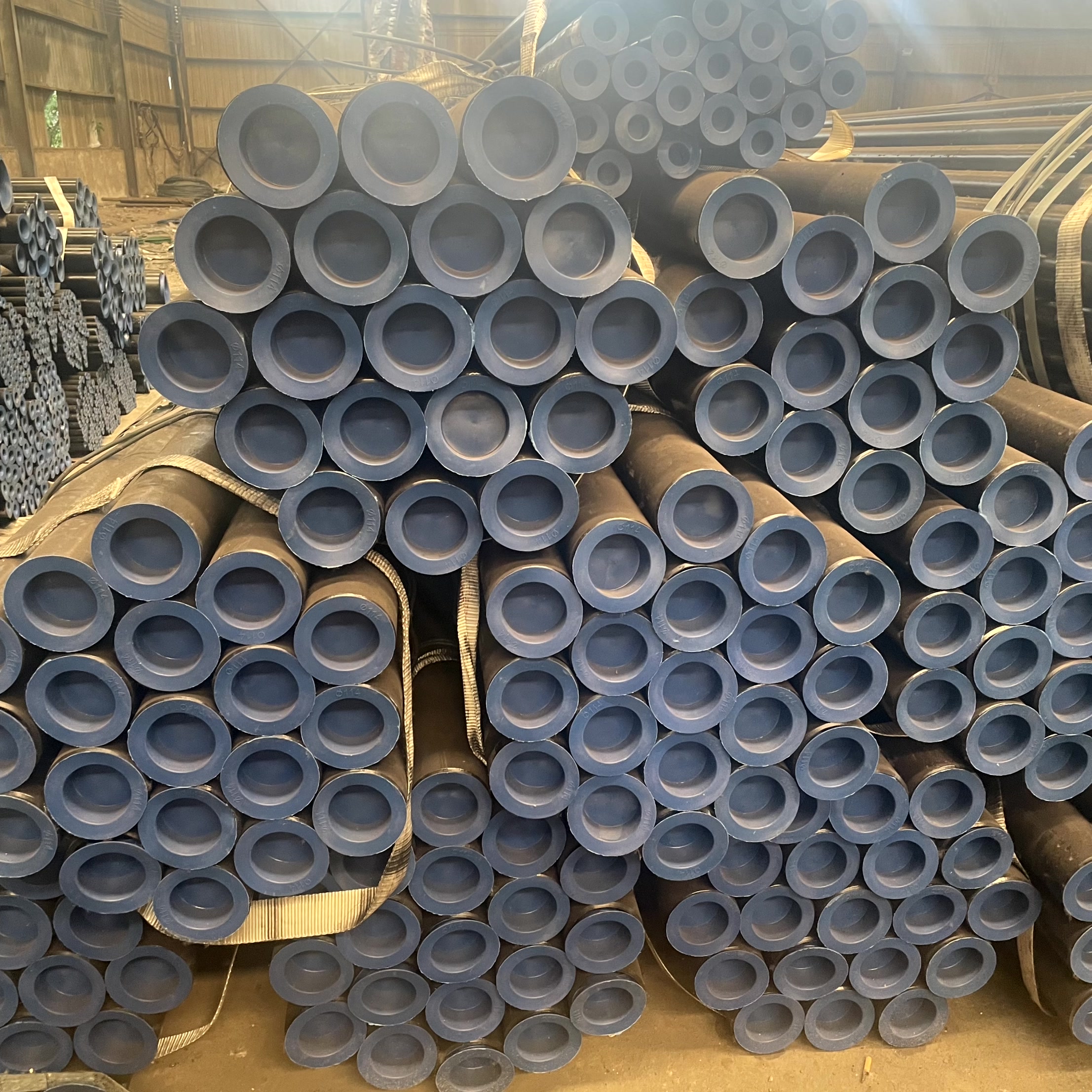
High-pressure pipeline systems are the "blood vessels" of industries such as energy and chemicals, and their design must balance safety, economy, and compliance. This article provides engineers with practical guidance from three aspects: design key points, comparison of international standards, and material selection, to ensure the long-term stable operation of pipelines under high-pressure environments.
Design Core
Wall Thickness Calculation: The wall thickness of high-pressure pipelines needs to be calculated comprehensively based on formulas (such as ASME B31.1) combined with design pressure, temperature, and material strength. Too thin a wall may lead to bursting risks, while too thick a wall increases cost and installation difficulty.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Technologies such as ultrasonic testing (UT) and magnetic particle testing (MT) are used to detect hidden defects in welds or base material (such as cracks and slag inclusions), ensuring pipeline integrity.
Hydraulic Pressure Test: After installation, a hydraulic pressure test at 1.5 times the design pressure is required to verify sealing and pressure resistance. This is the final safety barrier before commissioning.
Standard comparison
EN 10216-1 (European standard) vs. ASTM A106 (American standard): These two standards differ in material requirements and application scenarios:
EN 10216-1: The dominant standard in the European market, emphasizing low-temperature impact toughness (e.g., P235GH requires passing a 0°C impact test), compliant with the PED directive, suitable for steam systems and pressure vessels.
ASTM A106: A commonly used standard in North America, focusing on high-temperature performance (e.g., Grade B allows for higher carbon content), suitable for high-temperature conditions such as oil refining.
Standard selection recommendation: EN standards should be prioritized for European projects, while ASTM standards are required for exports to North America. Material traceability and certification levels (e.g., 3.1 certificate) should also be considered.
Material selection
P235GH carbon steel pipe: Compliant with EN 10216-1 standard, suitable for medium and low pressure steam systems (≤350℃), low cost and short delivery cycle, making it an economical choice for European projects; High-strength alloy pipe (such as 15CrMoG): Performs excellently in ultra-high pressure or high temperature (>400℃) scenarios, with significantly better creep resistance than ordinary carbon steel.
🔗 Product Related: For high-pressure system design, we recommend [EN 10216-1 P235GH Seamless Tube] or customized alloy steel pipe to balance performance and cost. 【Anchor Point】: [Return to the "Key Parameters for Selection" section of the support article to obtain the temperature and pressure resistance calculation method]
The balance between safety and efficiency
High-pressure pipeline design must prioritize safety while aiming for efficiency:
Strict adherence to standards reduces accident risks and avoids downtime losses; Appropriate material selection and testing technologies can extend pipeline lifespan and reduce overall lifecycle costs.
From wall thickness formulas to standard clauses, every step in high-pressure pipeline design requires precise control. By comparing European and American standards and selecting compliant materials, engineers can build a system architecture that is both safe and efficient.