Introduction
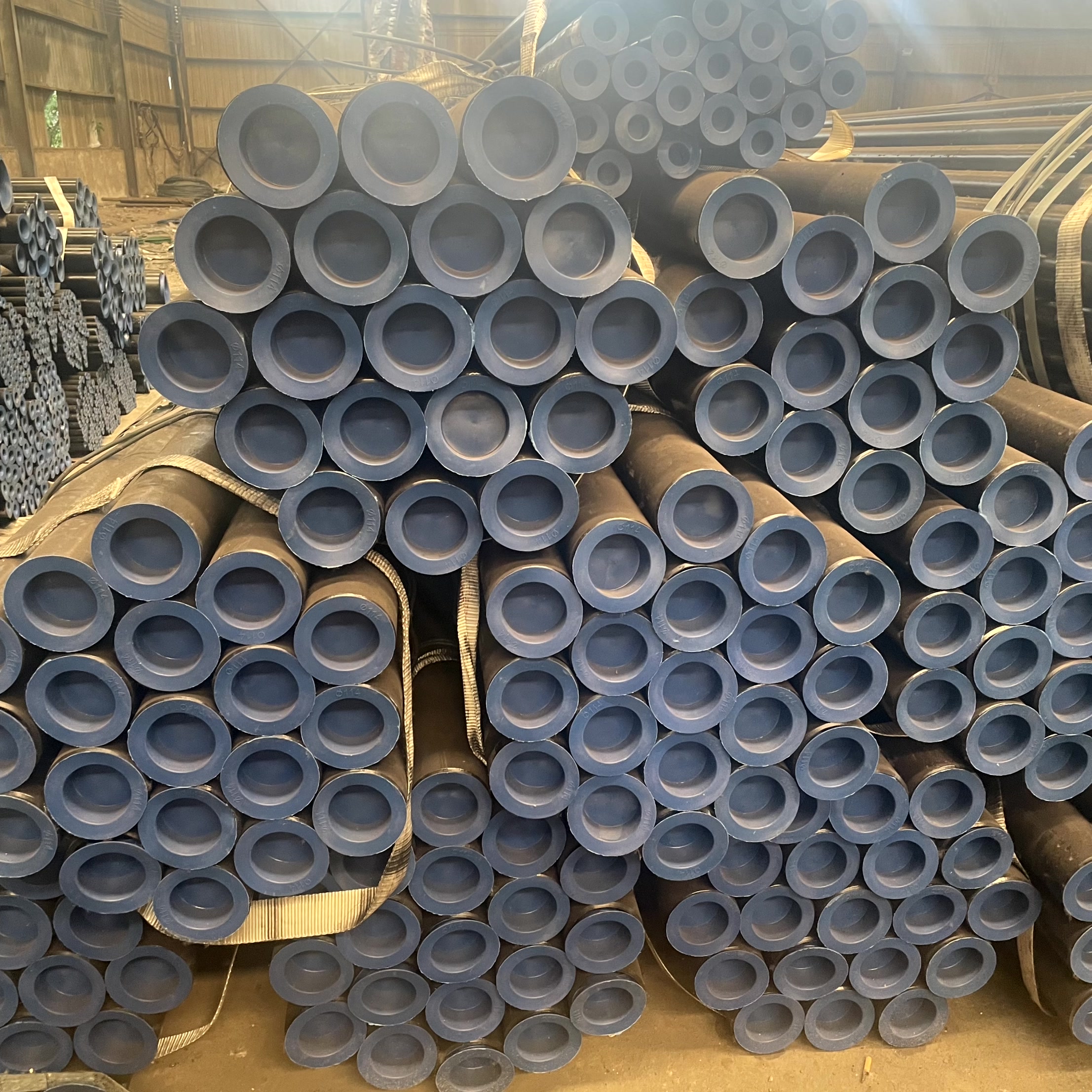
Throughout the vast history of industrial development, seamless steel pipes, as a crucial basic material, have played an indispensable role.From the structural support of skyscrapers to the lifeline of oil and gas transportation, from the core components of precision machinery to pressure vessels in the chemical industry, seamless steel pipes, with their superior performance and wide range of applications, have become an indispensable cornerstone of modern industry. This article aims to delve into the manufacturing process, application areas, unique advantages, and future development trends of seamless steel pipes, providing a comprehensive and in-depth understanding for those both inside and outside the industry. By analyzing every step of the seamless steel pipe manufacturing process, from raw material selection to the final product, it reveals the technological power and industrial wisdom behind it, while also envisioning a brilliant future for the seamless steel pipe manufacturing industry driven by advanced manufacturing technologies, new material research and development, and sustainable development concepts.
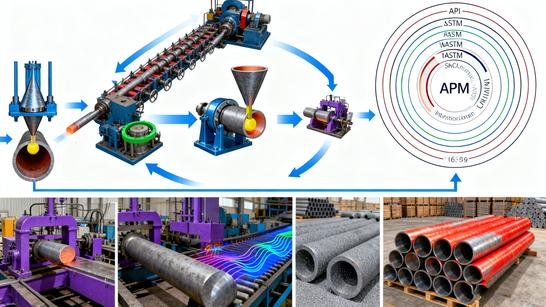
1. Construction of Seamless Steel Pipes
1.1 Raw Material Selection
The journey of crafting a seamless steel pipe begins with the meticulous selection of raw materials. High-quality steel billets, known for their purity and consistency, serve as the foundation. These billets are carefully inspected to ensure they meet stringent quality standards, as any impurities or inconsistencies could compromise the final product's integrity.
1.2 Heating and Piercing
Once the raw materials are deemed suitable, they undergo a heating process in a furnace, reaching temperatures that render them malleable.Subsequently, the heated billet is pierced using a specialized tool, transforming it into a hollow tube. This initial tube, though crude in appearance, marks the genesis of the seamless steel pipe.
1.3 Rolling and Sizing Processes
The hollow tube then embarks on a journey through a series of rolling and sizing processes. Rolling mills, equipped with precision-engineered rollers, gradually elongate and shape the tube, achieving the desired dimensions and specifications. This process demands utmost precision, as even minute deviations could affect the pipe's performance in its intended application.
2. Manufacturing Process of Seamless Steel Pipes
2.1 Hot Rolling
Hot rolling stands as a cornerstone technique in the manufacturing of seamless steel pipes, renowned for its ability to produce pipes with uniform grain structures and enhanced mechanical properties.The process initiates with the careful selection of high-quality steel billets, which are heated in a furnace to temperatures typically exceeding 1,000 degrees Celsius. This extreme heat renders the steel malleable, allowing it to be easily shaped and formed.
Once the steel billet reaches the desired temperature, it is transferred to a rolling mill. Here, the billet is progressively reduced in diameter and elongated through a series of rolling passes. The rolling mill consists of multiple stands, each equipped with precision-engineered rollers that apply controlled pressure to the billet. As the billet passes through each stand, its diameter decreases while its length increases, transforming it into a seamless tube.
The hot rolling process not only shapes the steel but also refines its microstructure. The high temperatures during rolling promote the formation of a uniform grain structure, which is crucial for the pipe's mechanical properties. A uniform grain structure enhances the pipe's strength, toughness, and resistance to fatigue, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Moreover, hot rolling enables the production of pipes with consistent wall thicknesses and diameters. This consistency is vital for ensuring the pipe's performance in its intended application, as any deviations could lead to leaks, bursts, or premature failure. The precision achieved through hot rolling minimizes the need for post-production machining, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
2.2 Cold Drawing
Following hot rolling, some seamless steel pipes undergo cold drawing, a process that further refines the pipe's dimensions and surface finish.Cold drawing involves pulling the hot-rolled pipe through a die, which is a precisely machined opening that imparts the desired shape and size to the pipe.
The cold drawing process begins with the selection of a suitable die, which is chosen based on the pipe's final dimensions and specifications. The hot-rolled pipe is then lubricated to reduce friction and facilitate smooth passage through the die. As the pipe is pulled through the die, it undergoes plastic deformation, achieving precise dimensions and an improved surface finish.
Cold drawing offers several advantages over hot rolling alone. Firstly, it enables the production of pipes with tighter tolerances, ensuring that the pipe's dimensions are within specified limits. This precision is crucial for applications where exact dimensions are essential, such as in hydraulic systems or precision instrumentation.
Secondly, cold drawing enhances the pipe's mechanical properties. The plastic deformation during cold drawing increases the pipe's tensile strength and hardness, making it more resistant to external forces and pressures. This improvement in mechanical properties extends the pipe's service life, particularly in demanding environments.
Finally, cold drawing improves the pipe's surface finish. The process eliminates surface imperfections, such as scratches or roughness, resulting in a smoother and more aesthetically pleasing appearance. This improved surface finish is beneficial for applications where appearance matters, such as in architectural or decorative uses.
2.3 Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes play a pivotal role in modifying the microstructure of seamless steel pipes, thereby improving their mechanical properties and making them suitable for specific applications. The most common heat treatment processes include annealing, normalizing, and quenching.
Annealing involves heating the pipe to a specific temperature and holding it there for a predetermined period, followed by slow cooling. This process relieves internal stresses, improves ductility, and reduces hardness, making the pipe easier to machine or form. Annealing is particularly useful for pipes that will undergo further processing, such as bending or threading.
Normalizing, on the other hand, involves heating the pipe to a higher temperature than annealing and then cooling it in air. This process refines the grain structure, improving the pipe's strength and toughness. Normalizing is often employed for pipes that will be used in applications requiring high strength and resistance to fatigue.
Quenching, the most aggressive heat treatment process, involves heating the pipe to a critical temperature and then rapidly cooling it in water or oil. This process produces a hard and brittle microstructure, known as martensite, which significantly increases the pipe's hardness and wear resistance. However, quenching also introduces internal stresses, which must be relieved through tempering, a subsequent heat treatment process that involves reheating the pipe to a lower temperature and holding it there for a specified period.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes of seamless steel pipes—hot rolling, cold drawing, and heat treatment—are sophisticated techniques that contribute to the pipes' final properties.
Each process plays a crucial role in ensuring the pipes' strength, durability, and suitability for specific applications. By understanding these processes, industry professionals can make informed decisions when selecting seamless steel pipes for their projects, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
3. Applications of Seamless Steel Pipes
3.1 General Structural Applications
Seamless steel pipes find widespread use in general structural applications, thanks to their high strength and durability.In construction projects, bridges, and buildings, these pipes provide unparalleled support and stability, ensuring the safety and longevity of structures even under the most demanding conditions. Their ability to withstand heavy loads and resist deformation makes them indispensable in the realm of civil engineering.
3.2 Pressure Vessel Piping
In the European standard pressure vessel industry, seamless pipes such as the EN 10216-1 P235GH play a critical role. Designed to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures, these pipes ensure the safe operation of pressure vessels, which are vital components in various industrial processes. Their seamless construction eliminates the risk of weld failures, a crucial factor in applications where safety is paramount.
3.3 Oil & Gas Pipeline Transportation
The transportation of oil and gas demands pipes capable of withstanding high pressures and corrosive environments. Seamless pipes like the API 5L X42/X52 emerge as the preferred choice, thanks to their exceptional pressure resistance and corrosion resistance. These pipes ensure the efficient and safe delivery of hydrocarbons over vast distances, playing a pivotal role in the global energy supply chain.
3.4 Industrial & Structural Use
Seamless carbon steel pipes, exemplified by the ASTM A53 Gr.B, enjoy widespread usage in industrial applications.From machinery manufacturing to automotive components and fluid transportation systems, these pipes offer versatility and reliability. Their ability to withstand diverse operating conditions and resist wear and tear makes them indispensable in various industrial settings.
4. Advantages of Seamless Steel Pipes
Seamless steel pipes, distinguished by their absence of welded joints, offer a multitude of advantages over their welded counterparts. These benefits stem from their unique construction process, which results in pipes with superior mechanical properties, enhanced durability, and improved resistance to various environmental factors. In this section, we delve deeper into the advantages of seamless steel pipes, exploring how they contribute to their widespread adoption across diverse industries.
4.1 Higher Strength
One of the most significant advantages of seamless steel pipes is their higher strength. The absence of welded joints eliminates weak points that are inherently present in welded pipes. Welded pipes, by their nature, have a heat-affected zone (HAZ) around the weld seam, where the microstructure of the steel has been altered due to the heat input during welding. This alteration can lead to a reduction in strength and an increased susceptibility to cracking under stress.
In contrast, seamless steel pipes are formed through a continuous process that does not introduce any heat-affected zones. The steel billet is heated and then pierced, rolled, and sized without any interruption, resulting in a homogeneous microstructure throughout the pipe. This uniformity ensures that the pipe can withstand higher external forces and pressures without failing, making it ideal for applications where structural integrity is paramount.
For instance, in the construction of high-rise buildings and bridges, seamless steel pipes are often used as structural supports. Their higher strength enables them to bear heavy loads and resist deformation under stress, ensuring the safety and stability of the structure. Similarly, in the automotive industry, seamless pipes are used in components such as drive shafts and exhaust systems, where they must withstand the vibrations and stresses of daily use.
4.2 Better Pressure Resistance
Another key advantage of seamless steel pipes is their superior pressure resistance. The seamless construction eliminates the risk of weld failures, which can be a significant concern in high-pressure applications. Welded pipes, despite advancements in welding technology, still carry a small risk of defects in the weld seam, such as porosity, inclusions, or incomplete penetration. These defects can act as stress concentrators, leading to premature failure under high pressure.
Seamless steel pipes, on the other hand, are designed to withstand extreme internal pressures without leaking or bursting. The uniform grain structure and lack of welds ensure that the pressure is evenly distributed across the pipe wall, reducing the likelihood of failure. This makes seamless pipes ideal for applications in the oil and gas industry, where they are used to transport hydrocarbons over long distances under high pressure.
For example, in the construction of oil and gas pipelines, seamless steel pipes like the API 5L X42/X52 are preferred due to their high pressure resistance and corrosion resistance.These pipes ensure the efficient and safe delivery of hydrocarbons, minimizing the risk of leaks and spills that could have catastrophic environmental consequences. Similarly, in the chemical processing industry, seamless pipes are used to transport corrosive chemicals under high pressure, where any failure could result in significant downtime and costly repairs.
4.3 Enhanced Durability
Durability is another hallmark of seamless steel pipes. The uniform grain structure and lack of welds contribute to the pipe's longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance. Welded pipes, due to the presence of welds, are more prone to fatigue and stress corrosion cracking over time. The weld seam acts as a stress concentrator, and under repeated loading and unloading cycles, cracks can initiate and propagate, leading to failure.
Seamless steel pipes, by virtue of their seamless construction, are less susceptible to fatigue and stress corrosion cracking. The absence of welds eliminates the stress concentration points, and the uniform grain structure ensures that the pipe can withstand cyclic loading without degrading. This makes seamless pipes ideal for applications where they are subjected to repeated stress cycles, such as in machinery manufacturing and automotive components.
For instance, in the manufacturing of machinery, seamless steel pipes are used in hydraulic systems, where they must withstand the high pressures and cyclic loading of the hydraulic fluid. Their enhanced durability ensures that the hydraulic system operates reliably over an extended period, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Similarly, in automotive components, seamless pipes are used in fuel lines and brake lines, where they must withstand the vibrations and stresses of daily use without failing.
4.4 Improved Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is another critical advantage of seamless steel pipes. The absence of welds eliminates crevices where corrosion can initiate and propagate. Welded pipes, due to the presence of welds, have a higher risk of corrosion, particularly in harsh environments. The weld seam can act as a site for the accumulation of corrosive substances, leading to localized corrosion and pitting.
Seamless steel pipes, on the other hand, offer improved corrosion resistance due to their seamless construction. The uniform surface finish and lack of welds reduce the likelihood of corrosion initiation and propagation. This makes seamless pipes ideal for applications in corrosive environments, such as in the chemical processing industry and marine applications.
For example, in the chemical processing industry, seamless steel pipes are used to transport corrosive chemicals, where any corrosion could result in leaks and spills. Their improved corrosion resistance ensures that the pipes can withstand the corrosive substances without degrading, minimizing the risk of environmental contamination. Similarly, in marine applications, seamless pipes are used in offshore platforms and ships, where they must withstand the corrosive effects of seawater.
4.5 Conclusion
Seamless steel pipes offer a multitude of advantages over their welded counterparts, including higher strength, better pressure resistance, enhanced durability, and improved corrosion resistance. These benefits stem from their unique construction process, which results in pipes with a homogeneous microstructure and lack of welds. As industries continue to demand pipes with superior performance and reliability, seamless steel pipes will remain the preferred choice for a wide range of applications. Understanding these advantages is crucial for industry professionals and enthusiasts alike, as it enables them to make informed decisions when selecting pipes for their specific needs.
5. Future Trends in Seamless Steel Pipe Manufacturing
5.1 Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
The seamless steel pipe manufacturing landscape is on the brink of a significant transformation, fueled by a wave of advanced manufacturing techniques that promise to redefine the industry's efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and design flexibility. Among these emerging technologies, laser welding and additive manufacturing stand out as game-changers, poised to revolutionize the way seamless pipes are produced.
Laser Welding Technology
Laser welding, with its precision and high-speed capabilities, offers a compelling alternative to traditional welding methods in the production of seamless steel pipes. While seamless pipes are inherently free of welds, certain manufacturing processes, such as the combination of different sections or the attachment of fittings, may still require welding. Laser welding, with its narrow heat-affected zone and minimal distortion, ensures a superior weld quality that is both strong and aesthetically pleasing. This technology enables manufacturers to produce pipes with thinner walls and tighter tolerances, enhancing their performance in applications where weight reduction and precision are critical. Moreover, laser welding's ability to join dissimilar materials opens up new avenues for creating composite pipes with tailored properties, such as enhanced corrosion resistance or thermal conductivity.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is another transformative technology that is gradually making its way into the seamless steel pipe manufacturing sector. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting away material from a solid block, additive manufacturing builds components layer by layer, directly from digital designs. This approach offers unparalleled design freedom, enabling the creation of complex geometries that were previously impossible or cost-prohibitive to produce using conventional methods. In the context of seamless steel pipes, additive manufacturing could facilitate the production of pipes with internal features, such as integrated sensors or flow channels, that enhance their functionality and performance. Additionally, additive manufacturing's ability to use a wide range of materials, including advanced alloys and composites, allows for the customization of pipes to meet specific application requirements, such as high-temperature resistance or superior mechanical properties.
Automation and Robotics
The integration of automation and robotics into seamless steel pipe manufacturing processes is another trend that is gaining momentum. Automated systems, equipped with advanced sensors and control algorithms, can perform tasks with greater precision, speed, and consistency than human operators, reducing the risk of errors and improving overall product quality. Robotics, in particular, can be deployed in hazardous or repetitive tasks, such as material handling, welding, and inspection, enhancing workplace safety and efficiency. The use of collaborative robots, or cobots, which work alongside human operators, further enhances flexibility and adaptability in manufacturing processes, allowing for rapid reconfiguration of production lines to accommodate different pipe sizes and specifications.
5.2 Material Innovations
The development of new steel alloys and composite materials is another key driver of innovation in the seamless steel pipe industry. These innovative materials offer superior properties, such as enhanced strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability, making seamless pipes suitable for even more demanding applications.
Advanced Steel Alloys
Researchers and manufacturers are continuously exploring new steel alloys that offer improved performance characteristics. For instance, high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels, which contain small amounts of alloying elements such as vanadium, niobium, or titanium, exhibit superior strength and toughness compared to conventional carbon steels. These alloys are particularly suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries, without compromising on structural integrity. Additionally, corrosion-resistant alloys, such as duplex stainless steels, which combine the properties of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, offer exceptional resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, making them ideal for use in harsh environments, such as offshore oil and gas platforms.
Composite Materials
Composite materials, which combine two or more distinct materials to create a new material with superior properties, are also gaining traction in the seamless steel pipe industry. For example, metal matrix composites (MMCs), which consist of a metal matrix reinforced with ceramic particles or fibers, offer enhanced strength, stiffness, and wear resistance compared to traditional monolithic metals. These composites can be tailored to specific application requirements by varying the type, size, and distribution of the reinforcing phase. Another promising composite material is the fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composite, which combines a polymer matrix with high-strength fibers, such as glass or carbon. FRP composites offer excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight construction, and design flexibility, making them suitable for applications where traditional steel pipes may be unsuitable or cost-prohibitive.
5.3 Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and resource depletion, the seamless steel pipe industry is increasingly focusing on sustainability and environmental considerations. Manufacturers are adopting energy-efficient manufacturing processes, using recycled materials, and implementing waste reduction strategies to minimize their environmental footprint.
Energy-Efficient Manufacturing Processes
Energy efficiency is a critical aspect of sustainable manufacturing. Seamless steel pipe manufacturers are investing in energy-efficient equipment and technologies, such as high-efficiency furnaces, heat recovery systems, and variable speed drives, to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the adoption of lean manufacturing principles, which emphasize the elimination of waste and the optimization of production processes, further enhances energy efficiency and reduces environmental impact.
Use of Recycled Materials
The use of recycled materials in seamless steel pipe manufacturing is another important sustainability trend. Recycled steel scrap, sourced from end-of-life products or manufacturing waste, can be melted down and reused to produce new pipes, reducing the need for virgin raw materials and conserving natural resources. Moreover, the use of recycled materials can significantly lower the carbon footprint of pipe production, as the energy required to process recycled steel is typically much lower than that required to extract and refine virgin iron ore.
Waste Reduction and Circular Economy
Seamless steel pipe manufacturers are also implementing waste reduction strategies and embracing the principles of the circular economy. By optimizing production processes, reducing scrap rates, and implementing recycling programs, manufacturers can minimize waste generation and maximize resource utilization. Additionally, the development of closed-loop systems, where waste materials are collected, processed, and reused within the manufacturing process, further enhances sustainability and reduces environmental impact.
In conclusion, the future of seamless steel pipe manufacturing is bright, driven by a convergence of advanced manufacturing techniques, material innovations, and sustainability considerations. As these trends continue to evolve, the seamless steel pipe industry will be well-positioned to meet the growing demands of various sectors, while contributing to a more sustainable and prosperous future.
6.Conclusion
Seamless steel pipes, as a crucial pillar of modern industry, showcase humanity's remarkable achievements in materials science through their sophisticated manufacturing processes, wide range of applications, and significant performance advantages. This article details the manufacturing process of seamless steel pipes, including key steps such as raw material selection, heating and piercing, rolling, and heat treatment, demonstrating the relentless pursuit of precision and quality in production.
Furthermore, we delve into the extensive applications of seamless steel pipes in structural engineering, pressure vessels, oil and gas transportation, and industrial machinery, highlighting their vital role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of social infrastructure.
Importantly, the significant advantages of seamless steel pipes compared to welded steel pipes, such as higher strength, better pressure resistance, greater durability, and corrosion resistance, make them the preferred material for many demanding applications.These advantages stem not only from their seamless structural design but also from the precise control of the material's microstructure during manufacturing.
Looking to the future, the seamless steel pipe manufacturing industry stands at a new historical starting point, facing unprecedented development opportunities and challenges.With the introduction of advanced technologies such as laser welding and additive manufacturing, as well as the research and application of new alloy materials and composite materials, the production efficiency, product quality, and customization capabilities of seamless steel pipes will be significantly improved.
Simultaneously, the growing acceptance of sustainable development concepts is prompting the industry to transform towards a greener and lower-carbon direction, achieving a win-win situation for both economic and environmental benefits through energy conservation, emission reduction, and resource recycling.
In conclusion, the seamless steel pipe manufacturing industry is in an era of rapid development and transformation. Through continuous innovation and upgrading, the industry will be able to better meet market demands, drive the continuous progress of related industries, and contribute more to the prosperity and development of human society.