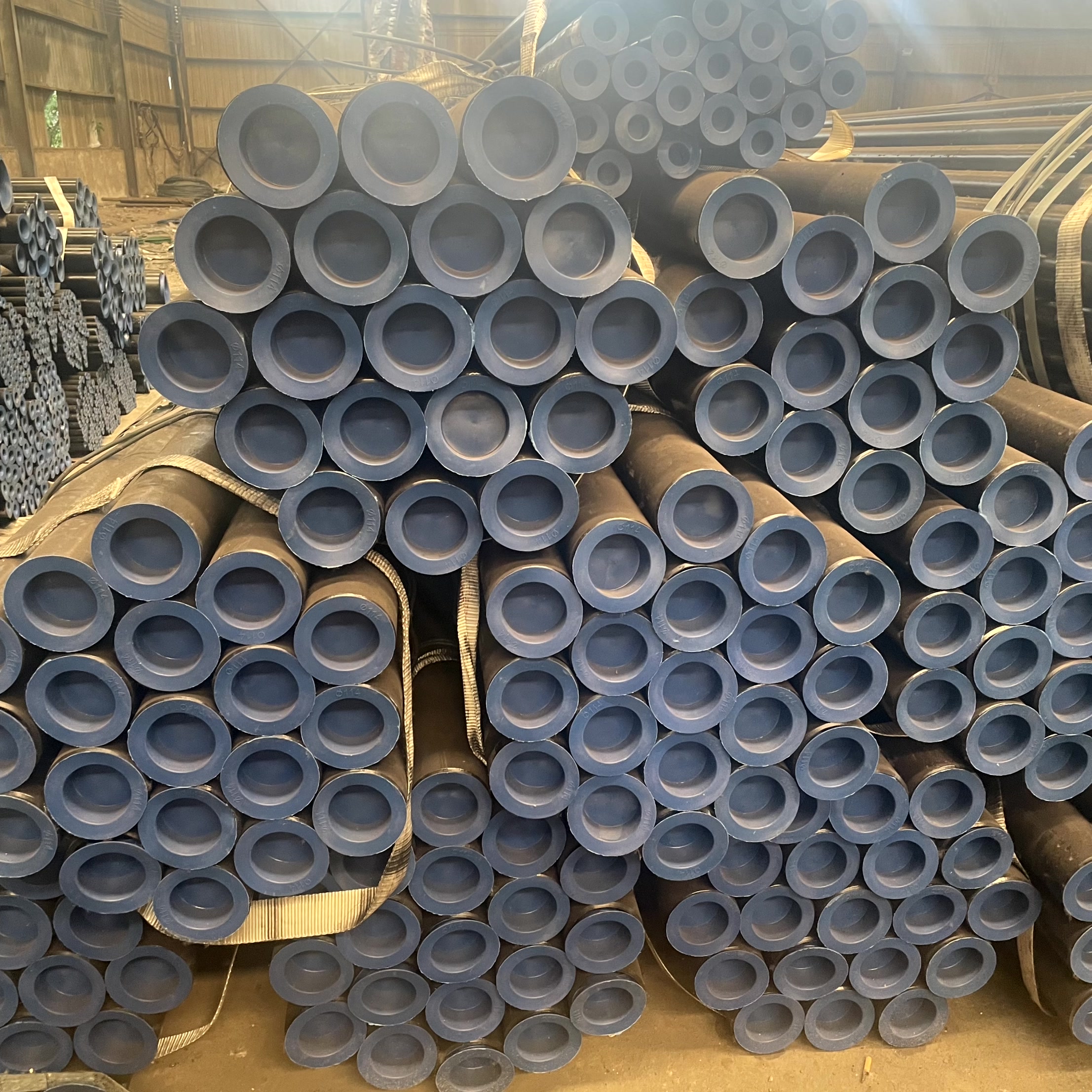
Cangtie Steel Pipe Company stands at the forefront of industrial fluid solutions as a premier manufacturer and exporter of ASTM A106/A53 & API 5L Seamless Steel Pipes. Our specialized inventory features high-performance Hot-Dipped Galvanized Seamless Pipes designed to exceed the rigorous safety standards of global energy and infrastructure projects.
1. A106's "heat resistance" and API 5L's "toughness" at low temperatures.
In power plant boilers, refinery furnaces, and complex thermal pipeline networks, pipes are not only carriers of fluids but also "lifelines" that withstand extreme stresses.
- Resisting "Creep": Material Strength at Temperatures Above 350°C Deep within refinery furnaces, pipes are constantly subjected to high temperatures and pressures. When metal is exposed to conditions exceeding half of its recrystallization temperature for extended periods, extremely small, permanent plastic deformation occurs, known as creep.
- The Crucial Role of Silicon (Si): Compared to ordinary carbon steel, ASTM A106 Gr.B strictly requires a minimum silicon content of 0.10%. As an excellent deoxidizer, silicon not only improves the purity of the steel but also strengthens the ferrite matrix at the microscopic level.
- Hardness Retention: This precise chemical composition ensures that the grain boundaries of A106 Gr.B remain stable in the temperature range of 350°C to 450°C. It effectively prevents the metal lattice from slipping under high-temperature stress, thus maintaining material hardness and ensuring that the pipe wall does not thin or bulge due to prolonged heating, significantly extending the maintenance cycle of the thermal system.
2. Challenging Thermal Expansion and Contraction: The "Inherent Advantage" of Seamless Structures
Power plant boilers and thermal pipe networks experience drastic temperature fluctuations during startup and shutdown. This frequent **thermal cycling** poses a significant challenge to the physical structure of the pipes.
- Eliminating "Stress Concentration" Points: Welded steel pipes have a heat-affected zone (HAZ) at the weld seam, where the metallographic structure differs from the base material. During frequent thermal expansion and contraction, the slight difference in expansion coefficients on either side of the weld seam creates significant stress concentration.
- The Integrity of Seamless Structures: Our seamless steel pipes are manufactured from a single steel billet through a piercing process, resulting in perfect isotropic properties. This means that when faced with the expansion forces generated by thermal expansion and contraction, stress is evenly distributed across the circumferential pipe wall. This effectively avoids the "stress fatigue cracks" common in welded pipes, providing a higher safety factor and leak protection in high-frequency fluctuating thermal pipe networks.
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: Extra Protection for Outdoor Heating Pipelines
For heating pipelines exposed to the outdoors, high temperatures bring not only internal stress but also accelerated external oxidation.
- Chemical Stability at High Temperatures: Our hot-dip galvanizing treatment forms a dense iron-zinc alloy layer on the steel pipe surface. Even in alternating hot and humid environments, this "galvanized armor" prevents acidic corrosion of the pipe wall from the external atmosphere, ensuring that the mechanical properties of the internal A106 Gr.B material are not compromised by external corrosion.
- Cracking the "cold brittleness" problem: The low-temperature toughness logic of API 5L
Most carbon steels transition from a ductile state to a brittle state when the temperature drops to a certain critical point. For oil and gas pipelines in high-latitude regions, if the material is not properly selected, even slight vibrations or pressure fluctuations can cause the pipe to shatter instantly like glass, leading to catastrophic leaks. - Impact Energy (Charpy V-Notch Impact Energy): Our API 5L seamless steel pipes feature a special metallurgical design for low-temperature environments. By controlling the carbon (C) content and increasing the proportion of manganese (Mn), we effectively lower the ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) of the steel.
- The Power of Microalloying: In high-grade API 5L pipes (such as X52 or higher grades), we add small amounts of microalloying elements such as niobium (Nb) and vanadium (V). These elements significantly refine the grain structure, allowing the material to maintain extremely high impact absorption energy even at extremely low temperatures of -45°C. This means that even in extreme cold, the pipes can absorb energy through material deformation when subjected to external impacts or crustal movements, rather than undergoing brittle fracture.
Seamless Technology: Eliminating "Stress Traps" at Low Temperatures
In liquefied gas circulation systems, where safety requirements are extremely high, any minor structural discontinuity can become a fatal flaw.
- No welds, no risk: Welded steel pipes are most susceptible to cracking at low temperatures, starting from small defects in the weld (such as incomplete penetration or porosity). Our API 5L seamless pipes, however, possess a perfectly continuous structure, completely eliminating the heat-affected zone (HAZ) at the weld.
- Uniform crack resistance: The seamless process ensures consistent physical properties throughout the 360-degree circumference of the pipe. During start-up and shutdown processes with significant temperature variations, the pipe body contracts uniformly, greatly reducing the risk of fracture caused by stress concentration.
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: A Corrosion Protection Barrier in Extremely Cold Regions
In high-latitude regions, pipelines often face corrosion from snow accumulation, ice formation, and de-icing salts. - Sacrificial Anode Protection: Our hot-dip galvanized API 5L pipes maintain excellent adhesion even at extremely low temperatures. The zinc coating not only prevents electrochemical corrosion caused by melting snow but also provides a physical barrier in the extremely cold, dry air, protecting the integrity of the internal steel.
It is these extreme operating conditions that define our rigorous product specifications—from the high-temperature stability of ASTM A106 to the low-temperature impact toughness of API 5L, every specification parameter is set to ensure that your engineering system has ample performance margin when facing the challenges of the natural environment.